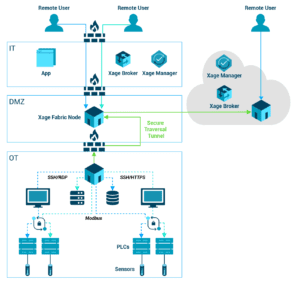
Here are 7 tips for maturing your zero trust security controls for remote access:
- Disable remote access protocols (RDP, SSH, VNC, etc.) as a default on computing devices
- Implement a remote access solution that doesn’t require inbound Internet connections. These solutions typically direct...
- Inject managed credentials to initiate the remote access session, always...
Full Answer
How to get started with zero trust security?
The different areas are:
- Secure identity with Zero Trust
- Secure endpoints with Zero Trust
- Secure applications with Zero Trust
- Secure data with Zero Trust
- Secure infrastructure with Zero Trust
- Secure networks with Zero Trust
- Visibility, automation, and orchestration with Zero Trust
What is zero trust mean?
“Zero trust means you have to get into a system that locks you out until you prove otherwise,” he says, referring to proof that the persons seeking access are who they say they are and can prove it.
What is a zero trust security strategy?
What is a Zero Trust Architecture
- A Zero Trust Architecture. In Zero Trust, you identify a “protect surface.” The protect surface is made up of the network’s most critical and valuable data, assets, applications and services ...
- Zero Trust: As Dynamic as Your Enterprise. Zero Trust is not dependent on a location. ...
- Deploying Zero Trust. ...
What is a zero trust security solution?
Zero trust security solutions may grant or deny access based on criteria such as:
- User identity
- Geographic location
- Time of day
- Operating system and firmware version
- Device posture
- Endpoint hardware type

What is a zero trust network Access?
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is an IT security solution that provides secure remote access to an organization's applications, data, and services based on clearly defined access control policies.
Is VPN or zero trust best for remote working security?
While VPNs do offer a level of connectivity, zero trust is specifically designed to meet modern needs for visibility and control as well as critical business demands such as remote work, speed, performance, security and more.
Is zscaler a zero trust?
Zscaler is the only cybersecurity vendor that offers a zero trust platform born in the cloud and designed for cloud organizations.
What are the advantages of zero trust?
Benefits of Zero Trust ArchitectureReduced threat surface.Maximized use and authority of authentication.Increased visibility into all user activity.The ability to dynamically provide access based on current use case.Reduce an attacker's ability to move laterally within your organization.More items...•
Will zero trust replace VPN?
VPNs don't address network security as deeply as zero trust network access (ZTNA), relying mostly on broad network-based protection. This means zero trust can be an excellent and more secure replacement for a VPN.
Is there something better than a VPN?
Two of the most common choices are software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). SD-WAN is designed to be a more efficient alternative to the VPN. Instead of implementing point-to-point connectivity, SD-WAN provides optimal routing of encrypted traffic between a network of SD-WAN appliances.
What technologies does zero trust require?
Zero Trust also requires consideration of encryption of data, securing email, and verifying the hygiene of assets and endpoints before they connect to applications. Zero Trust is a significant departure from traditional network security which followed the “trust but verify” method.
What is zero trust and how does IT work?
Zero Trust is a strategic approach to cybersecurity that secures an organization by eliminating implicit trust and continuously validating every stage of a digital interaction.
Who invented zero trust?
History. In 1994 (April ) the term "zero trust" was coined by Stephen Paul Marsh in his doctoral thesis on computer security at the University of Stirling.
What are the disadvantages of Zero Trust security?
The core challenge of zero trust is locking down access without bringing workflows to a grinding halt. People require access to sensitive data to work, communicate and collaborate. If individuals change roles and find themselves locked out of files or applications for a week, their productivity can plummet.
Which are the three components of Zero Trust?
There are three key components in a zero trust network: user/application authentication, device authentication, and trust.
Is Zero Trust widely accepted?
The Zero-Trust model has been widely recognized as an effective approach to prevent data breaches and mitigate the risk of supply chain attacks.
How is zero trust different than VPN?
VPN and zero-trust capabilities exist on opposite sides of the network security spectrum; VPNs enable connectivity for authorized remote users and managed devices, while zero-trust networks restrict access to all users at all times.
What is zero trust a model for more effective security?
Zero Trust is a security concept centered on the belief that organizations should not automatically trust anything inside or outside its perimeters and instead must verify anything and everything trying to connect to its systems before granting access. “The strategy around Zero Trust boils down to don't trust anyone.
Who created zero trust?
In 2010, John Kindervag, an analyst at Forrester Research, coined the term "zero trust," which centered around the idea that an organization shouldn't trust anything inside or outside its perimeters.
Why Zero Trust
Today’s organizations need a new security model that more effectively adapts to the complexity of the modern environment, embraces the hybrid workplace, and protects people, devices, apps, and data wherever they’re located.
Zero Trust principles
Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
Zero Trust defined
Instead of assuming everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originates from an open network.
Zero Trust defense areas
Verify and secure each identity with strong authentication across your entire digital estate.
Inform your strategy and adoption
Alex Simons, Corporate Vice President for Identity Security at Microsoft, and Steve Turner, analyst at Forrester Research, discuss the adoption of Zero Trust and offer practical advice for organizations to get started.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust (ZT) is an approach to network security and access control that meets the challenges of 21st Century cybersecurity. Also called Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) this new framework is based on one fundamental assumption:
What are the guiding principles behind Zero Trust?
The concept of “zero” trust has nothing to do with the emotional, social, and psychological nature of human trust. In the machine-to-machine context, trust is an algorithmically-generated evaluation of an incoming connection.
What are the benefits of Zero Trust?
Combining least privilege access, verify explicitly, and assume breach in a Zero Trust framework addresses the security weaknesses of legacy technologies. But the benefits of Zero Trust go much further.
What technology does Zero Trust technology replace?
The need for Zero Trust is driven by the failure of traditional access control technologies to keep pace with the way organizations work today. When Network Access Control (NAC), Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and similar technologies were developed, the corporate computing landscape was much different.
What are the key questions to ask when considering a Zero Trust provider?
What started out as a series of whitepapers a decade ago has become a dynamic, rapidly-evolving Zero Trust ecosystem. Choosing the right solution will deliver all the benefits we discussed earlier. Choosing the wrong approach to Zero Trust leads to wasted money on projects that are ultimately abandoned.
Why have companies been slow to adopt the Zero Trust model?
Google broke new ground by being the first Zero Trust implementation by a major enterprise. Unfortunately, the BeyondCorp initiative also set expectations that Zero Trust implementations are complicated, time-consuming, and expensive.
How can your organization implement ZTNA today?
Twingate simplifies ZTNA adoption by offering a Zero Trust solution that organizations can deploy in minutes. Using software-defined perimeters, Twingate hides your critical resources not only from the public internet but from your private networks as well.
What is zero trust?
The concept of zero-trust is centered around the idea that an organization should not trust anything or anyone by default, both inside and outside of its infrastructure. Before granting access to the organization’s infrastructure, identity, device, apps, and other specifications must be verified.
What is IAM in security?
IAM is a core technology that supports zero-trust access. IAM calls for creating one unique digital identity per person. After that identity is created, it can be used to connect to remote systems along with other verifying attributes such as location.
Common Remote Access Technologies Run Counter to Zero Trust
The urgency to “go remote” in response to the COVID-19 pandemic compelled organizations to lean into VPNs and remote access technologies, like remote desktop protocol (RDP), more heavily than ever. This seismic workplace shift magnified the considerable, pre-existing security faults inherent to many remote access technologies.
How to Align Remote Access with Zero Trust
A zero trust architecture (ZTA) treats all access requests as potentially malicious—a stark departure from the all-or-nothing access allowed by VPNs.
What is ZTNA's darknet?
IPs are never exposed to the internet, creating a “darknet” which makes the network impossible to find. ZTNA’s native app segmentation ensures that once users are authorized, application access is granted on a one-to-one basis. Authorized users have access only to specific applications rather than full access to the network.
What is ZTNA architecture?
ZTNA’s are most often 100% software-defined, eliminating the enterprises overhead of managing appliances. ZTNA’s also result in inbound stack simplification as organizations no longer require their VPN, DDoS, Global Load balancing, and FW appliances. There are two key ZTNA architecture models.
How does ZTNA reduce third party risk?
ZTNA significantly reduces third-party risk by ensuring external users never gain access to the network and that only authorized users gain access to permitted applications. With traditional M&A’s, integration can span multiple years as organizations must converge networks and deal with overlapping IPs.
How does ZTNA work?
ZTNA improves flexibility, agility and scalability, enabling digital ecosystems to work without exposing services directly to the internet, reducing risks of distributed denial of service attacks. Even from an architecture perspective, ZTNA works fundamentally different from network-centric solutions.
What is ZTNA in business?
ZTNA gives users seamless and secure connectivity to private applications without ever placing them on the network or exposing apps to the internet. While the path to zero trust as an ideology is vague, ZTNA provides a clear, defined framework for organizations to follow.
Is VPN slow for users?
VPN alternative. Organizations want to eliminate or lessen their VPN usage. Since VPNs are slow for users, offer poor security, and are difficult to manage, Gartner predicts that “By 2023, 60% of enterprises will phase out most of their remote access VPNs in favor of ZTNA.”. Secure Multi-cloud access.
Protecting Privileged Access for All Remote Sessions
When applying the granularity of privileged access management (PAM), including secure remote access, a zero trust approach ensures all access is appropriate, managed, and documented. Regardless of how the perimeter has been redefined.
What is the NIST Model
The U.S. Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines zero trust architecture in their 800-207 publication. The NIST zero trust model focuses on protecting network resources rather than network segments. This narrows network defenses to focus on individuals or groups of resources.
Zero Trust Approach Considerations
Remote users, dissolving network perimeters, and cloud-based assets are all drivers of zero trust strategies. Together, zero trust and secure remote access tools solve most remote worker and remote session challenges for both on-site and out-of-office workers.